The FactSage FSlead lead alloy database
Summary
TO OBTAIN :
- A LIST OF all the unary, binary AND ternary SYSTEMS WHICH HAVE BEEN ASSESSED
- A LIST OF ALL ASSESSED phases IN EACH OF THE SYSTEMS
- A CALCULATED PHASE DIAGRAM FOR EACH OF THE LISTED BINARY SYSTEMS
- ASSiSTANCE WITH PHASE SELECTION
CLICK ON “List of optimized systems and calculated binary phase diagrams.”.
General
The FactSage FSlead alloy database is directed primarily to the liquid state of lead-rich alloys, for which a large amount of assessed thermodynamic data is already available. It is based on relevant sub-systems from the old SGTE Solution Database, but now incorporating updates of those systems as well as many new published and in-house assessments. In particular, the assessed information contained in Dessureault ’s thesis [1] for the liquid phase of Pb-rich ternary systems has also been incorporated and a few new assessments have been carried out as part of the present work.
While the optimized thermodynamic parameters contained in FSlead are intended primarily to provide a sound basis for calculations relating to lead production and refining, lead-rich solid phases are also included in the database. This makes possible the calculation of liquidus temperatures and solidification characteristics relevant to the casting of certain lead-rich alloys, although, because of the more limited amount of assessed data for solid ternary and higher-order phases available, the results should be treated with caution.
Please note that the FSlead database is a self-consistently evaluated database designed to be used independently of any other. Considerable caution must be exercised if it is used in conjunction with other FactSage alloy databases. However, calculations involving the gas phase can be performed with the FACTPS Database.
The elements included as alloying components of lead are:
Ag, As, Au, Bi, C, Ca, Cd, Cu, Fe, Ga, Ge,
H, Hg, In, Ni, O, S, Sb, Se, Sn, Sr, Te, Tl, Zn
From the previous version of the FSlead Database, the following elements have been removed: Al, Mn, Pd, Si and Zr. However, hydrogen (H) has been added.
The lead-containing binary systems are described over all ranges of composition and temperature, i.e. the assessed data provide a good description of the complete phase diagram and thermodynamic properties for the binary alloy system concerned. The list of assessed binary sub-systems is given in a section below.
Specific information on each alloy system can be obtained from the list of references supplied further below.
[1] Y.Dessureault, Ph.D.Thesis, Ecole Polytech., Univ.Montreal, Nov.1993.
Composition Ranges
As mentioned above, the database is intended primarily for calculations relating to
Pb-rich liquid alloys. However, some uses may involve relatively large concentrations of the alloying elements present. For this reason, the majority of the assessed binary systems in the LEAD alloy database are described over the entire composition range of the alloys involved.
Ternary interaction parameters have been assessed for only a few Pb-rich Pb-A-B ternary systems. The number of such assessed parameters is particularly limited in the case of solid phases. Many other ternary interactions in Pb-rich Cu-A-B solutions are estimated, using the appropriate models, from the assessed binary parameters for Pb-free A-B phases. Note that calculation of phase boundaries in higher-order systems may give very unreliable results when the ternary interaction parameters for the solid solutions are estimated by combination of such binary parameters.
Temperature Ranges
The database is generally valid for the approximate temperature range from room temperature to 1500 C.
Modeling
In the assessments, the liquid phase has been described using the Modified Quasichemical Model in the Pair Approximation (MQMPA) which evaluates the effect of short-range order between 2 elements in the solution. Some binary assessments were made equivalent to a Bragg-Williams (random mixing) approximation when the published binary assessment dictated that choice.
The fcc Pb-rich phase and intermetallic phases have been described using a sublattice model (Compound Energy Formalism).
Systems assessed
The following matrix is an overview of the binary optimized subsystems in the FSlead
Database:
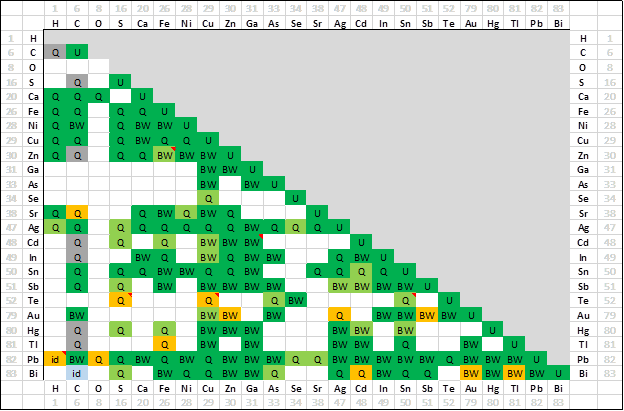

Phase Selection in the EQUILIB and PHASE DIAGRAM Modules
The FSlead database has been constructed in order to simplify the phase selection in the EQUILIB and PHASE DIAGRAM modules of FactSage:
If the database is used alone (i.e. without any other connected databases), you can simply select all pure solids and all solution phases (i.e. click on the button “Select” and the submenu item “Select all solutions”). If the activity of a pure liquid species is intended to be computed, then select all pure liquids.
If the database is used in conjunction with FACTPS, you can simply select all gaseous species and all pure solids. Then select all solution phases (i.e. click on the button “Select” and the submenu item “Add all solutions from database | FSlead”). If the activity of a pure liquid species is intended to be computed, then select all pure liquids. Select carefully the species and solutions from other databases (i.e. FToxid, FTsalt, etc.), however, avoid to include solutions and pure species from another alloy database (i.e. FSstel, FTlite, etc.) as there can be important differences between these databases and FSlead.
In the EQUILIB module for large systems (i.e. more than 5 elements), some solutions will see their default phase selection (“+, I, J, etc.”) changed from “I” (i.e. possible 2-phase immiscibility) to “!” (i.e. dormant (metastable) phase) as these solutions contain a very large number of end-members (hundreds to thousands of phase constituents). For these solutions, no mass can be attributed to them as they are set to be metastable. However, a post-calculation is performed in order to evaluate their activity. If their activity is greater than 1, then it is recommended that you repeat the calculation(s) with the phase selection overridden as “+” or “I” (by right-clicking on the “+”-column (2nd column) of the “Products | Solution phases” box of the MENU Window.
Assessed Binary Lead-containing Systems
Pb-Ag
Pb-As
Pb-Au
Pb-Bi
Pb-C
Pb-Ca
Pb-Cd
Pb-Cu
Pb-Fe
Pb-Ga
Pb-Ge
Pb-Hg
Pb-H
Pb-In
Pb-Ni
Pb-O (up to PbO)
Pb-S (up to PbS)
Pb-Sb
Pb-Se
Pb-Sn
Pb-Te
Pb-Tl
Pb-Sr
Pb-Zn
Assessed Ternary interaction Parameters in Pb-rich systems
(assessed parameters for certain phases only – click on “List of optimized systems and calculated binary phase diagrams” for details.)
Pb-Ag-As
Pb-Ag-Au
Pb-Ag-Bi
Pb-Ag-Cu
Pb-Ag-S
Pb-Ag-Sb
Pb-Ag-Sn
Pb-Ag-Zn
Pb-As-Cu
Pb-As-Fe
Pb-As-Sn
Pb-As-Zn
Pb-Au-Bi
Pb-Au-Cu
Pb-Au-In
Pb-Au-Zn
Pb-Bi-Cu
Pb-Bi-Fe
Pb-Bi-S
Pb-Bi-Sn
Pb-Bi-Zn
Pb-Cu-S
Pb-Cu-Sb
Pb-Cu-Sn
Pb-Cu-Zn
Pb-Fe-S
Pb-Fe-Sb
Pb-S-Sb
Pb-S-Sn
Pb-S-Zn
Pb-Sb-Zn
Pb-Sn-Zn
Other assessed binary interaction parameters from which ternary interactions in Pb-rich systems are estimated (please refer to the matrix of binary assessed subsystems).
References
Pure Element Data
A.T.Dinsdale, SGTE Data for Pure Elements, Calphad 15 (1991) 317-425
Binary Lead-containing Systems
Pb-Ag: H.L.Lukas, unpublished work, 1998; based on Zimmermann's thesis work.
Pb-As: Data supplied by M.Hamalainen (ca.1993), but corrected for SGTE lattice stabilities.
Pb-Au: J.P.Nabot, Thesis, Grenoble 1986.
Pb-Bi: D.Boa, I.Ansara, Thermochimica Acta 314 (1998) 79-86.
Pb-C: T.Chart, NPL, unpublished work (1987)
Pb-Ca: V.P.Itkin and C.B.Alcock, J. Phase Equilib. 1992, pp.162-169.
Pb-Cd: W. Zakulski, Z. Moser: J. Phase Equilib, 1995, 16(3), 239-242. W. Zakulski, Z. Moser: J. Phase Equilib, 1995, 16(6), 484.
Pb-Cu: P. Chartrand (2018)
Pb-Fe: P. Chartrand (2018)
Pb-Ga: I.Ansara, F.Ajersch, J. Phase Equilibria 12 (1991) 73-77.
Pb-Ge: P.Y.Chevalier, Thermochimica Acta 155 (1989) 227-240.
Pb-H: P. Chartrand, est. (2018)
Pb-Hg: A. Maitre, J. M. Fiorani, M. Vilasi: J. Phase Equilib., 2002, 23(4), 329
Pb-In: D.Boa, I.Ansara, Thermochimica Acta 314 (1998) 79-86.
Pb-Ni: Cui Ping Wang, Xing Jun Liu, I. Ohnuma, R. Kainuma, K. Ishida: CALPHAD, 2000, 24(2), 149-167
Pb-O: P. Chartrand (2018) – O solubility in Pb
Pb-S: P. Chartrand (2018)
Pb-Sb: H.Ohtani, K.Okuda, K.Ishida, J.Phase Equilibria 16 (1995) 416-429
Pb-Se: P. Chartrand (2018)
Pb-Sn: Based on H.Ohtani, K.Okuda, K.Ishida, J.Phase Equilib.16 (1995) 416-429
Pb-Te: P. Chartrand (2018)
Pb-Tl: unpublished work from I. Ansara, H.L. Lukas and S. G. Fries (comm. P.J. Spencer)
Pb-Zn: T.Jantzen, P.J.Spencer, Calphad 22 (1998) 417-434
Ternary Interaction Parameters in Lead-rich Systems
(assessed parameters for certain phases only – click on “List of optimized systems and calculated binary phase diagrams” for details.)
Ternary interaction parameters for the following systems have been derived using the
summarized information contained in the Ph.D thesis of Y.Dessureault, Ecole
Polytechnique, University of Montreal, November, 1993.
Pb-Ag-As Pb-As-Zn Pb-Cu-S
Pb-Ag-Au Pb-Au-Bi Pb-Cu-Sb
Pb-Ag-Bi Pb-Au-S Pb-Cu-Sn
Pb-Ag-S Pb-Au-Sn Pb-Fe-S
Pb-Ag-Sb Pb-Au-Zn Pb-Fe-Sb
Pb-Ag-Sn Pb-Bi-Cu Pb-S-Sb
Pb-Ag-Zn Pb-Bi-Fe Pb-S-Sn
Pb-As-Cu Pb-Bi-S Pb-S-Zn
Pb-As-Fe Pb-Bi-Sn Pb-Sb-Zn
Pb-As-Sn Pb-Bi-Zn
Ternary interaction parameters for other Pb-contianing systems are from the following publications:
Pb-Ag-Cu: F.H.Hayes, H.L.Lukas, G.Effenberg, G.Petzow, Z. Metallkde, 77 (1986) 749-754.
Pb-Au-In: J.P.Nabot, Thesis, Grenoble 1986.
Pb-Cu-Zn: T.Jantzen, P.J.Spencer, CALPHAD 22 (1998) 417-434.
Pb-Sn-Zn: T.Jantzen, P.J.Spencer, CALPHAD 22 (1998) 417-434.
Other Binary Parameters
(assessed parameters for certain phases only – click on “List of optimized systems and calculated binary phase diagrams” for details.)
Ag-As: P. Chartrand (2018)
Ag-Au: Re-assessed MQMPA liquid from S.Hassam, J.Agren, M.Gaune-Escard, J.P.Bros, Met.Trans. 21A (1990) 1877-1884
Ag-Bi: Wang, Jian & Cui, Senlin & Rao, Weifeng. (2018). Journal of Electronic Materials. 47.
Ag-C: P. Chartrand (2014)
Ag-Ca: J. Wang, P. Chartrand and I-H Jung, CALPHAD 50 (2015)
Ag-Cu: Wang, Jian & Cui, Senlin & Rao, Weifeng. (2018). Journal of Electronic Materials. 47.
Ag-Fe: P. Chartrand (2014)
Ag-Ga: W. Gierlotka, D. Jendrzejczyk-Handzlik, Journal of Alloys & Compounds 509 (2011) 38
Ag-Ge: P.Y.Chevalier, E.Fischer, private Communication, 1998:
Ag-H : P. Chartrand (2014)
Ag-Hg: Y. Liu et al. / Thermochimica Acta 547 (2012) 83–88
Ag-In: J. Wang, P. Hudon, D. Kevorkov, P. Chartrand, I-H Jung, M. Medraj, JPE 2014, 35(3), 284-313
Ag-Ni: Wang, Jian & Cui, Senlin & Rao, Weifeng. (2018). Journal of Electronic Materials. 47.
Ag-Pd: G. Ghosh, C. Kantner, G. B. Olson, J. Phase Equilib., 1999, 20(3), 295-308
Ag-S: P. Chartrand (2018)
Ag-Sb: E. Zoro, C. Servant, B. Legendre, Journal of Phase equilibria and Diffusion, 2007, 28, 250-257
Ag-Se: P. Chartrand (2018)
Ag-Sn: J. Wang, P. Hudon, D. Kevorkov, P. Chartrand, I-H Jung, M. Medraj, JPE 2014, 35(3), 284-313
Ag-Ti: Mei Li, Changrong Li, Fuming Wang, Weijing Zhang, CALPHAD, 2005, 29, 269-275
Ag-Tl: H.-L. Lukas, reassessment based on of Zimmerman’s thesis, 1976
Ag-Zn: J. Wang, Y-N Zhang, P. Hudon, I-H Jung, M. Medraj, P. Chartrand, J. Alloys Cmpds (2015) 639, p. 593
As-Au: P.J.Spencer, June 1998
As-Bi: P. Chartrand (2018)
As-Cu: M. Hämäläinen, private communication, 2004
As-Fe: P.J. Spencer (2008)
As-Ga: C Chatillon, I. Ansara, A. Watson and B. B. Argent: CALPHAD, 1990, 14(2), 203-14.
As-Ge: I. Ansara and D. Dutarte: CALPHAD, 1984, 8(4), 323-342.
As-In: C.Chatillon, I.Ansara, A.Watson, B.B.Argent, Calphad 14 (1990) 203-214
As-Sb: H.Ohtani, Calphad 18 (1994) 196
As-Te: P. Chartrand (2018)
Au-Bi: P.Y.Chevalier, Thermochimica Acta 136 (1988) 15-24
Au-C : P.J. Spencer (2007)
Au-Cu: B.Sundman, S.G.Fries, A.Oates, Calphad 22 (1998) 335-354
Au-Ge: P. Y. Chevalier: Thermochimica Acta, 1989, 141, 217-226.
Au-In: I.Ansara, J.P.Nabot, Calphad 16 (1992) 13-18
Au-Sb: P.Y.Chevalier, Thermochimica Acta 155 (1989) 211-225
Au-Sn: P.Y.Chevalier, Thermochimica Acta 130 (1988) 1-13
Au-Te : Y. Feutelais, D. Mounai, J. R. Didry, B. Legendre: J. Phase Equil., 1994, 15(4), 380-385. (with modified AuTe2)
Au-Ti: P.J.Spencer, July 1998
Au-Tl: P.Y.Chevalier, Thermochimica Acta 155 (1989) 211-225
Au-Zn : COST-531
Bi-Cd: P. Chartrand (2014)
Bi-Cu: J. Wang, CRCT (2015)
Bi-Fe: Li-Mei Pan, unpublished research (1991)
Bi-Ga: C. Girard: Thesis, Marseille 1985.
Bi-Ge: P. Y. Chevalier: Thermochimica Acta, 1988, 132, 111-116
Bi-Hg: unpublished assessment of S. A. Mucklejohn.
Bi-In: D.Boa, I.Ansara, Thermochimica Acta 314 (1998) 79-86
Bi-Ni: J. Wang, CRCT (2015)
Bi-S: P. Chartrand (2018)
Bi-Sb: P. Chartrand (2014) MQMPA refit from H.Ohtani, K.Ishida, J.Electronic Mater. 23 (1994) 747-755
Bi-Sn: J. Wang, CRCT (2015)
Bi-Tl: Zimmermann B., Henig E. T., Lukas H. L.: Z. Metallkde., 1976, 67(12), 815-820
Bi-Zn: C.Girard, Thesis, Marseille, 1985
C-Ca : P. Chartrand (2018)
C-Cu: Shubhank and Y.-B.Kang CALPHAD 45 (2014) 127–137
C-Fe: M-S Kim, Y-B Kang JPE 2015
C-Ge: P. Chartrand (2014)
C-Ni: B. J. Lee: CALPHAD, 1992, 16(2), 121-149.
C-Sb: P. Chartrand (2018)
C-Sn: P. Chartrand (2007)
C-Ti: P. J Spencer (2008)
C-Zr: A. Fernandez Guillermet: J. Alloys Compounds, 1995, 217, 69-89.
Cu-Ca: D.Risold, B.Hallstedt, L.J.Gauckler, H.L.Lukas, S.G.Fries, Calphad 20 (1996) 151-160
Ca-Fe: S.Cui, M.Paliwal and I.-H. Jung, MetTrans 2014
Ca-H: J.-P. Harvey, Master Thesis, Polytechnique Montreal (2006)
Ca-In: J. Wang, P. Chartrand and I-H Jung, CALPHAD 50 (2015)
Ca-Ni: M. Medraj (2006)
Ca-O: P. Chartrand (2000)
Ca-Sn: J. Wang, Ph.D. Thesis, Polytechnique Montreal (2014)
Ca-Ti: P. Chartrand (2014)
Ca-Zn: P.J. Spencer (2006)
Cd-Fe: P. Chartrand (2018)
Cu-Cd: X-M Chen, L-B Liu, L-G Zhang, H. Bo and Z-P Jin Trans Nonferrous Met Soc. China, 20 (2010) 649-654
Cd-Ga: Zakulski W., Moser Z., Rzyman K., Lukas H. L., Fries S. G., Sikiennik M., Kaczmarczyk R., Castanet R.: J. Phase Equil., 1993, 14(2), 184-196.
Cd-Ge: P. Chartrand (2018)
Cd-Hg: Jang J., Silk N. J., Watson A., Bryant A. W., Chart T. G., Argent B. B.: CALPHAD, 1995, 19(3), 415-430
Cd-In: Zakulski W., Moser Z., Rzyman K., Lukas H. L., Fries S. G., Sikiennik M., Kaczmarczyk R., Castanet R.: J. Phase Equil. 1993,14(2),184-196
Cd-S: P. Chartrand (2018)
Cd-Sb: L. A. Zabdyr: CALPHAD 1997, 21(3), 349-358.
Cd-Sn: P. Chartrand (2018)
Cd-Tl : Y. Liu et al. / Journal of Alloys and Compounds 473 (2009) 60–64
Cd-Zn: L. A. Zabdyr: CALPHAD 1997, 21(3), 349-358.
Cu-Fe: Shubhank and Y-B. Kang, CALPHAD 2014
Cu-Ga: Li et al., CALPHAD 32(2) (2008), 447-453
Cu-Ge: Wang et al. J.Alloys Cmpds 2010
Cu-H: J.-P. Harvey, Master Thesis, Polytechnique Montreal (2006)
Cu-Hg: Y. Liu et al. / Thermochimica Acta 547 (2012) 83–88
Cu-In: C.R.Kao, A.Bolcavage et al, J Phase Equilibria 14 (1993) 22-30
Cu-Ni: M. Mezbahul-Islam and M. Medraj, “Experimental study of the Cu-Ni-Y system at 700°C using diffusion couples and key alloys” Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 561(5), 161-173 (2013)
Cu-O: P. Chartrand (2018)
Cu-S: P. Waldner, internal report, CRCT (2005)
Cu-Sb: SGTE Solution Database, 2004.
Cu-Se: P. Chartrand (2018)
Cu-Sn: J. Wang, internal report, CRCT (2015)
Cu-Te: P. Chartrand (2018) and P.Coursol, Report from CRCT, Ecole Polytechnique de Montreal, August 2001.
Cu-Ti: H.C.Hari Kumar, I.Ansara, P.Wollants, L.Delaey, Z.Metallkde., 87 (1996) 666-672
Cu-Tl: P.Y.Chevalier, Thermochimica Acta 156 (1989) 383-392
Cu-Zn: Liang, Hsiao, Schmid-Fezter CALPHAD, 2015
Fe-H: J-P. Harvey, Master Thesis, Polytechnique Montreal (2006)
Fe-Hg: P. Chartrand (2018)
Fe-In: P. Chartrand (2018)
Fe-Ni: A.Dinsdale, T.Chart, NPL, unpublished work, 1986: I.Ansara - fcc ordering
Fe-S: P. Waldner and A.D.Pelton, "Thermodynamic Assessment of the Fe-Ni-S System", Metall. and Mat. Trans., 35B, 897-907 (2004).
Fe-Sb: P.J.Spencer, 1998
Fe-Sn: K.C.H.Kumar, P.Wollants, L.Delaey, Calphad 20 (1996) 139-149 (with modifs from P. Chartrand (2018))
Fe-Ti: L.F.S.Dumitrescu, M.Hillert and N.Saunders, J.Phase Equilibria 19 (1998) 441-448
Fe-Tl: P. Chartrand (2018)
Fe-Zn: P. Chartrand (2018) MQMPA calibrated on the solids of Xiong, Du Liu CALPHAD 2009
(later modifications by M.Jacobs)
Ga-Ge: I Ansara, J P Bros, M Gambino: CAPHAD, 1979, 3, 225-233
Ga-Hg: unpublished assessment of I. Ansara, (1991).
Ga-In: B. C. Rugg, T. G. Chart: CALPHAD, 1990, 14(2), 115-123
Ga-Sb: I. Ansara, C. Chatillon, H. L. Lukas, T. Nishizawa, H. Ohtani, K. Ishida, M. Hillert, B. Sundman, B. B. Argent, A. Watson, T. G. Chart, T. Anderson: CALPHAD, 1994, 18(4), 177-222
Ga-Sn: T. J. Anderson, I. Ansara: J. Phase Equilibria, 1992, 13(2), 181-189
Ga-Tl: I. Katayama et al., T. Iida, Z. Metallknd. 94, 2003, p.1296
Ga-Zn: Dutkiewicz, J., Moser, Z., Zabdyr, L., Gohil ,D. D., Chart, T. G., Ansara I., Girard, C.: Bull. Alloy Phase Diagrams, 1990, 11(1), 77-82
Ge-In: P. Y. Chevalier: 1989, 155, 227-240
Ge-Sb: P. Y. Chevalier, Thermochimica Acta, 1989, 155, 227-240.
Ge-Sn: Y. Feutelais, B. Legendre, S. G. Fries: CALPHAD, 1996, 20(1), 109-123
Ge-Tl: P. Chevalier, Thermochimica Acta, 1989, vol 155, pp. 227-240
Ge-Zn: P. Chevalier, Thermochimica Acta, 1989, vol 155, pp. 227-240
H-Ni : J-P. Harvey, Master Thesis, Polytechnique Montreal (2006)
H-Ti : J-P. Harvey, Master Thesis, Polytechnique Montreal (2006)
H-Zn : J-P. Harvey, Master Thesis, Polytechnique Montreal (2006)
Hg-S : P. Chartrand (2018)
Hg-Sn: Yee-Wen Yen, Joachim Grobner, Steve C. Hansen, and Rainer Schmid-Fetzer JPE, 24(2), p.151-167, 2003
Hg-Zn: S. C. Hansen: CALPHAD, 1998, 22, 359-373.
In-Pb: D.Boa, I.Ansara, Thermochimica Acta 314 (1998) 79-86
In-Sb: T.J.Anderson, Calphad 18 (1994) 206
In-Sn : Wang, J., Hudon, P., Kevorkov, D. et al. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. (2014) 35: 284
In-Zn : Wang, J., Hudon, P., Kevorkov, D. et al. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. (2014) 35: 284
Ni-S: P. Waldner and A.D. Pelton, "Thermodynamic Modeling of the Ni-S System", Z. Metallkunde, 95, 672-681 (2004).
Ni-Sn : COST-531
Ni-Ti: C.S.Oh, J.Korean Inst.Met.Mater. 33 (1995) 129-136
Ni-Zn: J. Miettinen: CALPHAD, 2003, 27, 263-274
S-Sb: P. Chartrand (2018)
S-Sn: P. Chartrand (2018)
S-Te: P. Chartrand (2018)
S-Zn: P. Chartrand (2018)
Sb-Sn: C.S.Oh, J.H.Shim, B.J.Lee, D.N.Lee, J.Alloys and Cpds. 238 (1996) 155-166
Sb-Zn: L.A.Zabdyr, Calphad 21 (1997) 349-358
Se-Te: G. Ghosh, R. C. Sharma, D. T. Li, Y. A. Chang: J. Phase Equil., 1994, 15(2), 213-224
Sn-Te: P. Chartrand (2018)
Sn-Ti: F.Hayes, COST 507 (1998) ISBN 92-828-3902-8, p.284-287
Sn-Tl: P. Chartrand (2018)
Sn-Zn: P Ghosh, MD Mezbahul-Islam, M Medraj - Calphad, 2012
Ti-Zn: K. Doi, S. Ono, H. Ohtani, M. Hasebe: J. Phase Equilib. Diff., 2006, 27(1), 63-74.
Other Ternary Parameters (assessed parameters for certain phases only – click on “List of optimized systems and calculated binary phase diagrams” for details.)
…upcoming